

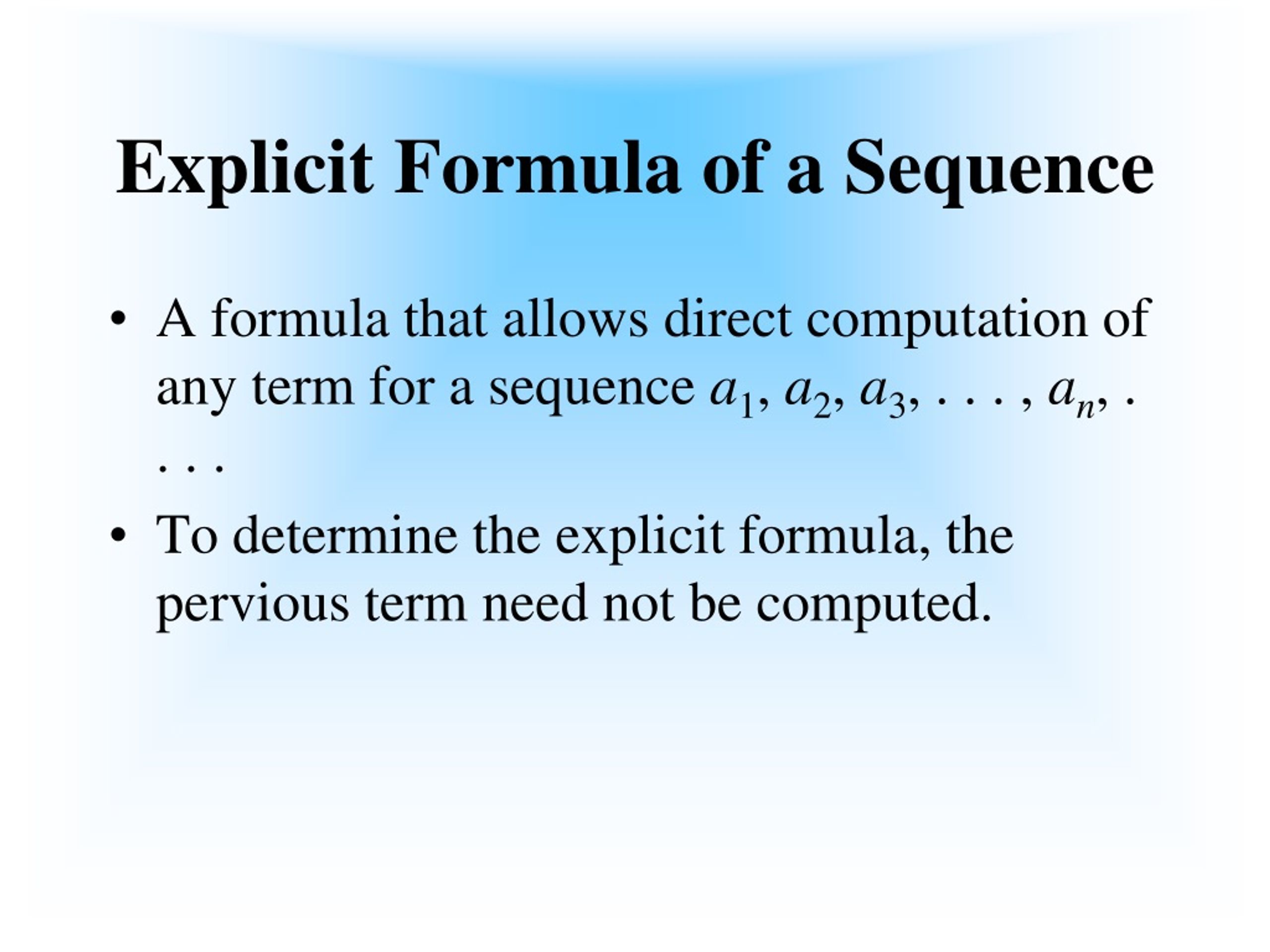
- Explicit formula for arithmetic sequence guided notes how to#
- Explicit formula for arithmetic sequence guided notes full#
- Explicit formula for arithmetic sequence guided notes zip#
Of field names to exclude from validation. The optional exclude argument allows you to provide a set Uniqueness constraints defined via Field.unique,įield.unique_for_date, Field.unique_for_month,įield.unique_for_year, or Meta.unique_together on your model instead of individualįield values. This method is similar to clean_fields(), but validates pub_date is not None : if exclude and "status" in exclude : raise ValidationError ( _ ( "Draft entries may not have a publication date." ) ) else : raise ValidationError ( ) Model. clean_fields ( exclude = exclude ) if self.
def clean_fields ( self, exclude = None ): super (). Update, you could write a test similar to this:Ĭlass Article ( models. It is possible to force the set of fields to be loaded by using the fieldsįor example, to test that an update() call resulted in the expected
Using argument can be used to force the database used for reloading. The default database if the instance wasn’t loaded from the database. The reloading happens from the database the instance was loaded from, or from Otherĭatabase-dependent values such as annotations aren’t reloaded. Only fields of the model are reloaded from the database.
Explicit formula for arithmetic sequence guided notes full#
The example above shows a full from_db() implementation to clarify how that _loaded_values ): raise ValueError ( "Updating the value of creator isn't allowed" ) super (). (This example doesn't # support cases where 'creator_id' is deferred). For example, # prevent changing the creator_id of the model.
Explicit formula for arithmetic sequence guided notes zip#
_loaded_values = dict ( zip ( field_names, ( value for value in values if value is not DEFERRED )) ) return instance def save ( self, * args, ** kwargs ): # Check how the current values differ from.

db = db # customization to store the original field values on the instance instance. reverse () values = instance = cls ( * values ) instance. concrete_fields ): values = list ( values ) values.
Explicit formula for arithmetic sequence guided notes how to#
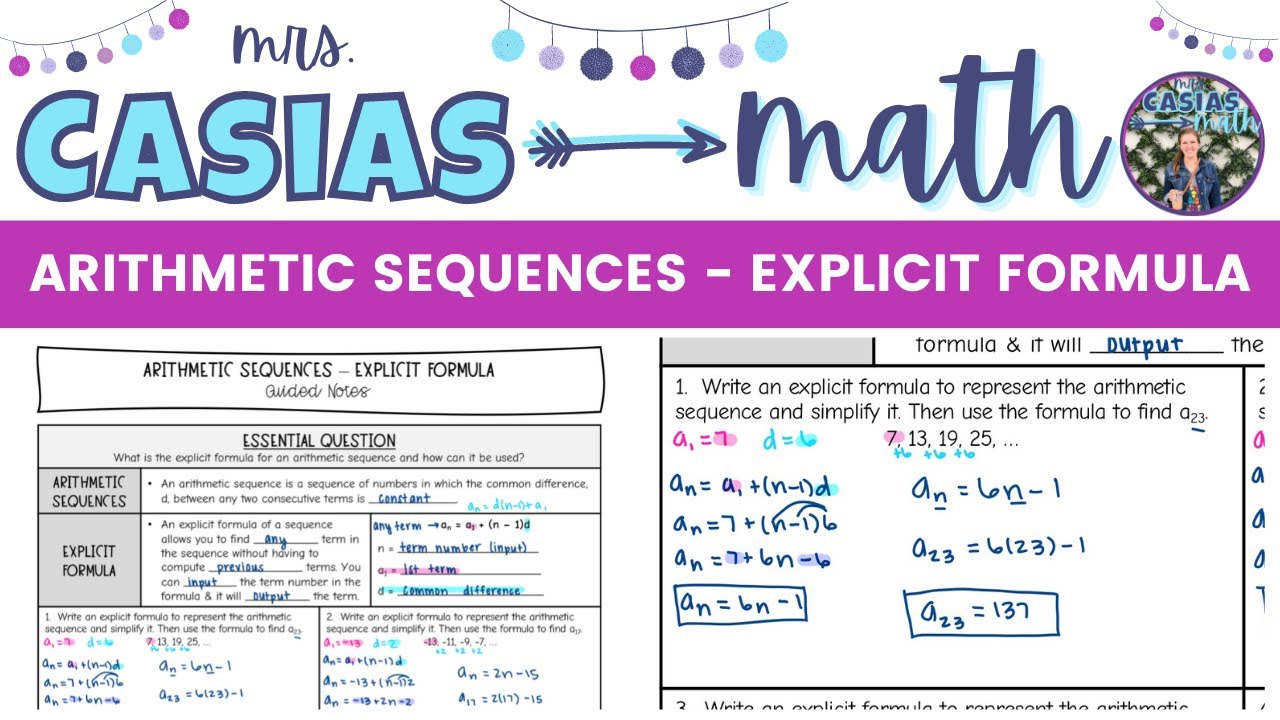
In addition to creating the new model, the from_db() method must set theĪdding and db flags in the new instance’s _state attribute.īelow is an example showing how to record the initial values of fields thatįrom django.db.models import DEFERRED def from_db ( cls, db, field_names, values ): # Default implementation of from_db() (subject to change and could # be replaced with super()). In that case, assign a value of django.db.models.DEFERRED If any fields are deferred, they won’t appear inįield_names. That is, the instance can be created byĬls(*values). If all of the model’sįields are present, then values are guaranteed to be in the order Theįield_names are in the same order as the values. Values contains the loaded values for each field in field_names. Is loaded from, field_names contains the names of all loaded fields, and The db argument contains the database alias for the database the model The from_db() method can be used to customize model instance creation Students will have a complete set of notes from which to study.Customizing model loading ¶ classmethod Model.Students will ask more questions during instructional periods.Help both student and teacher stay focused.Landscape Orientation - Horizontal layout for Interactive Whiteboards, Chromebooks and tablets.Students will write arithmetic sequences, both recursively and with an explicit formula, construct a linear function based on an arithmetic sequence, and use arithmetic sequences to model real-world situations.Students will understand that arithmetic sequences are functions, sometimes defined recursively.Students investigate the double and add 5 game in a simple case.Given the common difference and the value of the first term generate the terms in the sequence and then write a recursive and explicit formula for the sequence.Use a recursive process to find the next 3 terms in a sequence and then write a recursive and explicit formula for the sequence.Use a recursive process to find the next 3 terms in a sequence, graph the sequence and write a recursive and explicit formula.Use the recursive process to find the next 3 terms in a sequence and write an recursive and explicit formula.Use the Recursion to find the next 3 terms in a given sequence.Find the pattern of the Fibonacci Sequence.Use the Double and Add 5 Rule to generate a sequence.Arithmetic Sequences: Recursive & Explicit Formulas – Interactive Guided Notes


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
